The Science of IPMP + zinc
New in-vitro evidence for IPMP solution
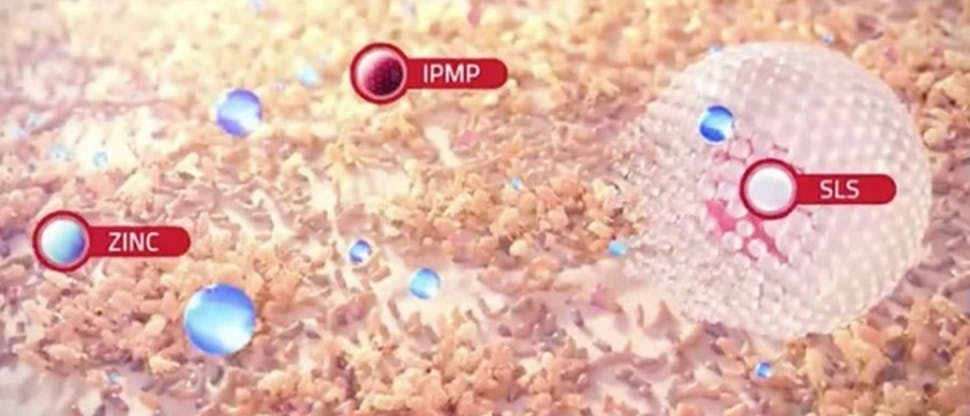
IPMP is a known broad spectrum antibacterial1,2 and antiplaque ingredient3 and in-vitro studies have shown that it inhibits the anaerobic bacterial* species4 typical of mature plaque1 which can compromise gingival health.4,5
Haleon scientists were keen to understand more about WHY & HOW IPMP impacts gingival health
New in-vitro research gives some additional insight4
- Treatment with IPMP solution was shown to be associated with an increase in the proportion of early colonisers, such as streptococci4
- These bacteria are characteristic of early plaque formation and are linked to gingival health5
Learn more about the action of an IPMP + zinc mouthwash by watching the mode of action video in the link above.

Daily brushing and flossing
Daily brushing and flossing are the fundamental foundation of a patient’s gum health between oral health visits. In line with your home care guidance, additional steps, such as an anti-bacterial daily zinc mouthwash, may help enhance the patients’ daily oral care routine to help keep gums healthy.6,7
Biofilms form naturally on oral surfaces to create a complex microbiome.8 Although historical treatment strategies for oral diseases focused on elimination, it is now understood that the presence of health-associated oral microbiota or modifying disease-associated communities should be the focus.8,9
Read more about the role of lifestyle factors in gum disease risk.
parodontax Active Gum Health delivers the antibacterial ingredient to hard-to-reach areas
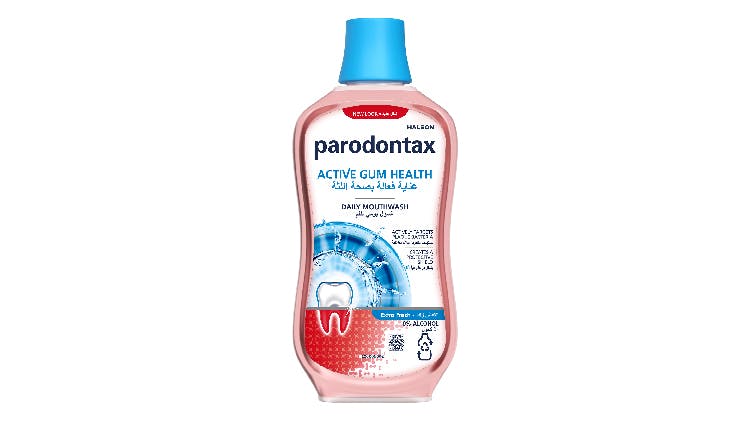

parodontax Active Gum Health daily mouthwash
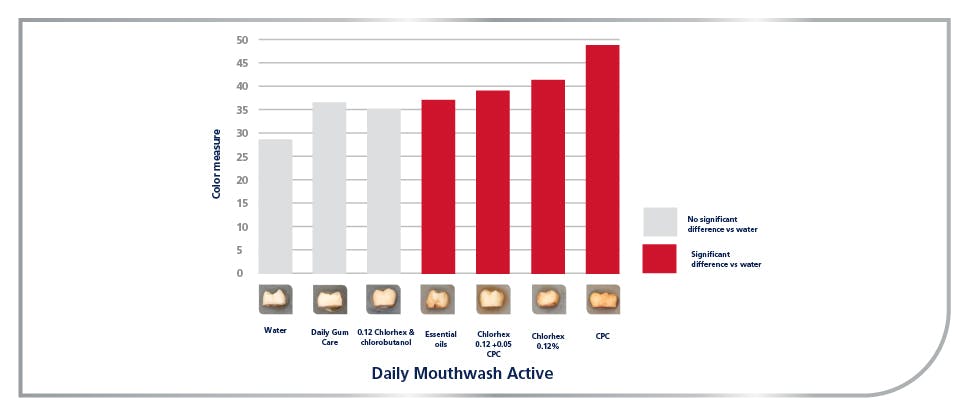
- Scientifically proven to keep gums healthier*
- Delivers the antibacterial ingredient IPMP + zinc along the gumline as well as hard to reach areas
- With zinc for fresh breath protection and fluoride to strengthen teeth
- Delivers great taste and leaves a cooling sensation
*compared to brushing alone
In line with your home care guidance, additional steps may help enhance the effectiveness of brushing
Gum health overview
Whilst plaque is the leading cause of gum disease, it is not the only causal factor for the progression of periodontitis.15 Find out more about the condition and patient impacts.
The parodontax range
Find out how the parodontax mouthwash range can help your patients to enhance their oral care.

Mission: Gingival Health
This space has been created and designed so you can find the latest news in periodontology, including insights and commentary from experts, conferences and events.