Panadol for children

Tough** on fever and pain,1 gentle1,3¶ on the child†
Panadol for children contains paracetamol, which is recommended as first-line treatment for fever and mild-to-moderate pain in children.2-4 It starts to relieve fever within 15 minutes of dosing.1,5-7
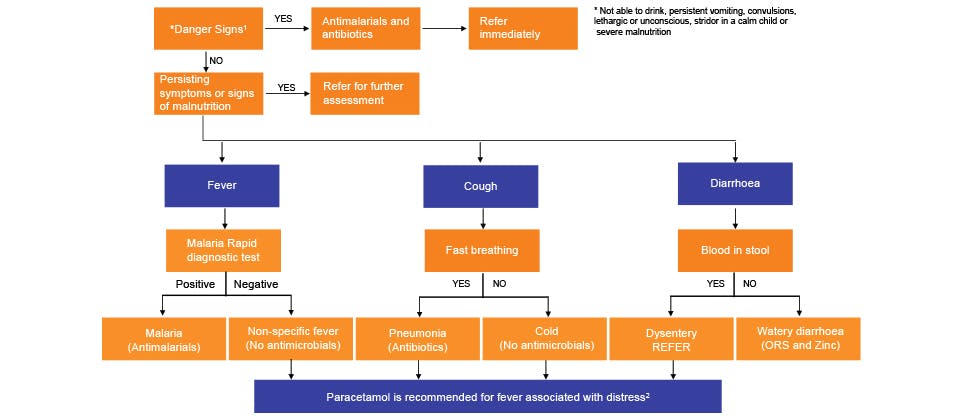
The World Health Organization guidelines on fever management state that when a child presents with fever, danger signs should be looked for. These include an inability to drink, persistent vomiting, convulsions, lethargy or unconsciousness, stridor in a calm child or severe malnutrition. If these signs are present, the patient must be referred immediately for specialist management.8
The symptomatic fever, associated with distress due to non-specific respiratory infections, diarrhoea and other infections, is managed with paracetamol.2
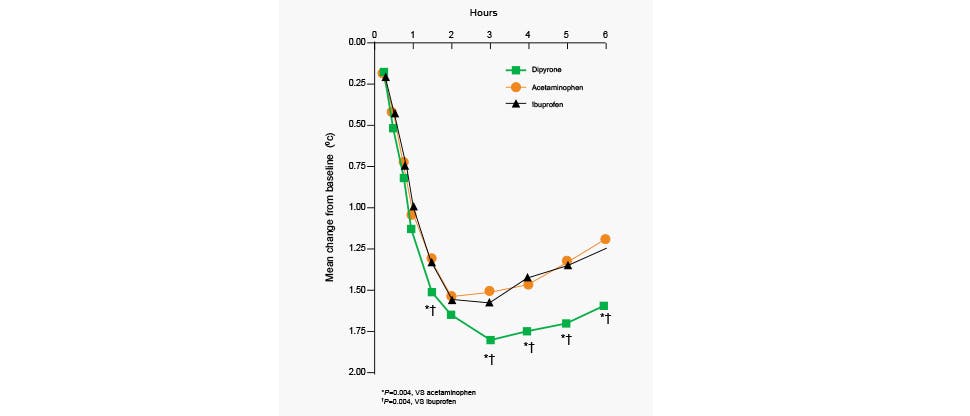
This was a randomised, double-blind multicentre trial involving febrile children aged 6 months to 6 years who were given a dose of paracetamol (acetaminophen) 12 mg/kg (n=210). A downward slope in temperature was seen at the 15-minute time point. Maximal rate of temperature reduction was reached at 60 minutes in the paracetamol group.6
As effective as ibuprofen at doses of 10 mg/kg9
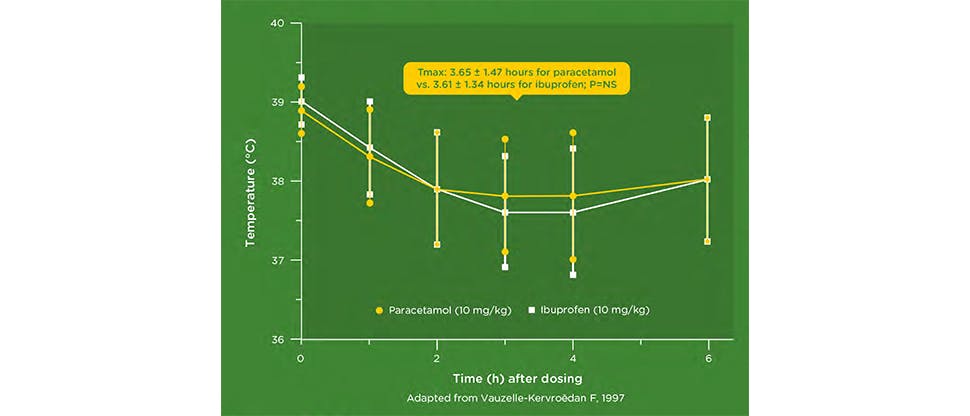
This was a randomised, double blind, multicentre trial with 116 children aged 4.1 years (± 2.6 years) with a fever related to an infectious disease and a mean baseline temperature of 39°C (± 0.5°C), who were treated with either single doses of ibuprofen 10.3 mg/kg (± 1.9 mg/kg) or paracetamol 9.8 mg/kg (± 1.9 mg/kg). The children’s rectal temperature was regularly monitored for 6 hours. Tmax is the time that elapsed between first dose of drug administration and lowest temperature observed between the 0-6 hours.9
When given to children with fever, both paracetamol 10 mg/kg and ibuprofen 10 mg/kg were similar in reduction of temperature in the time between dosing and achieving lowest temperature during 0-6 hours.9

In a literature review of 23 clinical studies of paracetamol involving children, the safety data showed that paracetamol had comparable safety to ibuprofen and ketoprofen in short-term treatment of fever.3

Ollie’s got a fever
Ollie’s 1 years old and has been having a fever for the past two days. His mum is worried because he’s been fussy and not eating well. She wants something to help him get rid of the fever and at the same time, something that is suitable for him.
Panadol Baby & Infant suspension
Children’s Panadol 5-12 years Elixir
Learn more

Clinical Study

When to refer children with fever
Learn more about “red-flag” symptoms when children present with fever.

Educate your patients on migraines
Specially tailored for your patients’ use, this simple to read patient resource will add value to migraine management.
