Panadol for Migraine
A new dimension in migraine treatment
The powerful triple action of paracetamol, acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) and caffeine working together to help combat migraine.1,2 It was shown to be more effective than ibuprofen 400 mg.3
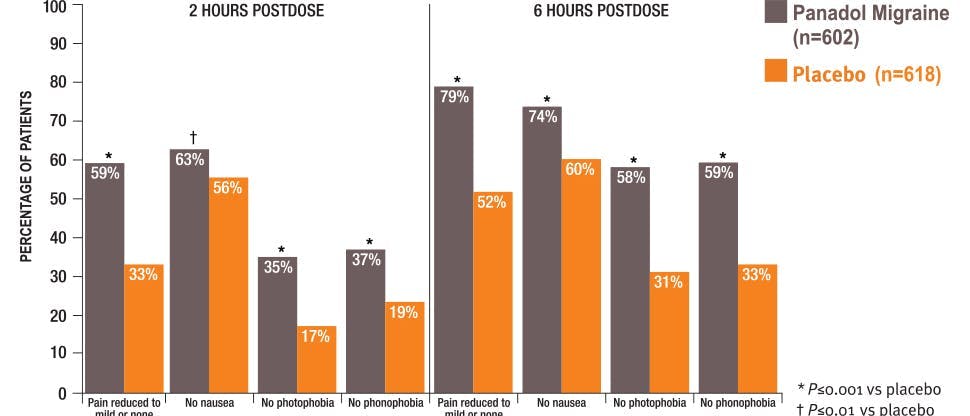
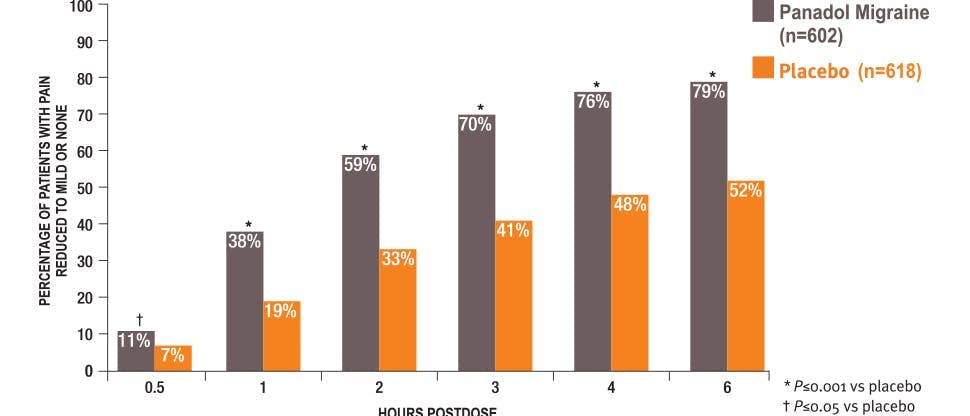
Significantly improves migraine-associated symptoms1
Panadol Migraine significantly improved pain and migraine associated symptoms such as nausea, sensitivity to light and sensitivity to sound.1

Rebecca needs migraine relief
When it attacks, Rebecca gets a throbbing headache on the right side, feels sick and finds noise and light hard to bear. As a young mother to a newborn, she’s tired and stressed, waiting for the next migraine attack. All she wanted was to enjoy motherhood but with sleepless nights, the migraines are getting bothersome.
Rebecca wants something that she can tolerate and effective to help manage her migraines.
Panadol Migraine contains a powerful triple action combination of medicines to help Rebecca manage her migraine pain. It also could help her manage the other symptoms associated with the attacks.
Recommend Panadol Migraine to combat migraine headaches
Panadol Migraine
The powerful triple action of paracetamol, acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) and caffeine working together to help combat migraine.1,2
Learn more
Request Samples
Provide your patients with a product sample when you make your expert recommendation to encourage them to make changes for better oral health and pain relief.
Management of migraine
Learn more about how paracetamol, acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) and caffeine work together to treat migraines.