Panadol Cold & Flu

Contains 3 active ingredients for multi-symptom relief
Combining 3 active ingredients into one convenient dose helps patients to simplify treatment.18 Panadol Cold & Flu contains:
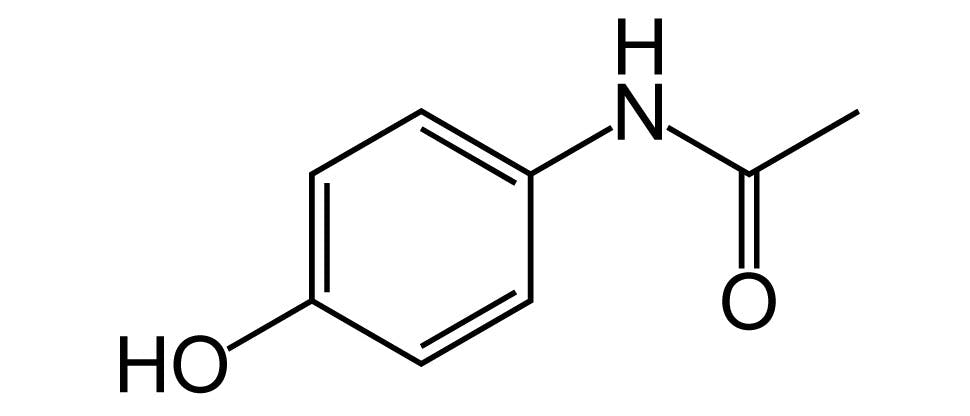
- Paracetamol to manage pain and fever19
- Pseudoephedrine hydrochloride for decongestion of the nose and sinuses19
- Chlorphenamine Maleate for reduction of cold and flu symptoms such as a runny nose15,19

Panadol Cold & Flu (paracetamol 500mg, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride 30mg, chlorphenamine maleate 2mg)
For patients who are looking for effective multi-symptom relief of colds and flu that allows them to get the rest they need.1-17
Panadol Cold & Flu – Your Cold & Flu Partner
The Panadol Cold & Flu range
Find out how the Panadol Cold & Flu range can help your patients.